

- #FILE DUPLICATE FINDER MAPREDUCE CHECKSUM PORTABLE#
- #FILE DUPLICATE FINDER MAPREDUCE CHECKSUM WINDOWS#
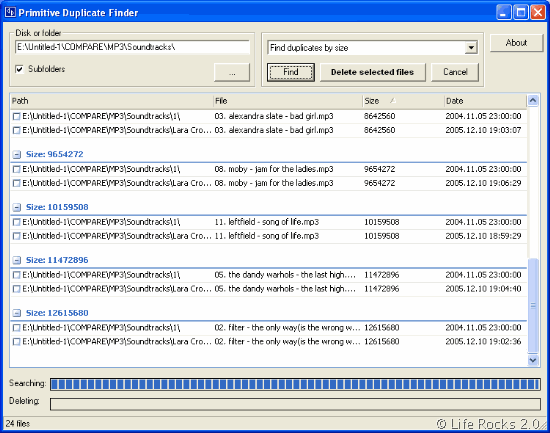
Hit the Ok button, and Dupe Clear will switch to the tab. You'll see a popup that displays the results of the process, including the total number of files searched, number of duplicate files that were found and the amount of storage space that can be recovered by deleting said files. Give it half a minute, and it will finish the scan. The program takes a while to finish the process, especially if the selected folders have hundreds of files. The other options are used to compare the file names, creation date, last modified date and the file type.Ĭlick the Start button to initiate the scan. The first one checks for the file's contents based on their SHA-1 hash values, while the other option takes into account files from multiple folders. There are several rules that you can set for the scan, two of which are pre-enabled match same contents, and match across folders. By default, Dupe Clear will scan inside sub-folders, so if you don't want recursive scanning, you might want to toggle the option. Click the "Add Folder" button and select a directory, you can add multiple folders to be scanned. The main tab is called Search Location, and as the name implies, this is where you select directories that you want the program to scan for duplicate files. It has a minimalist GUI, with 4 tabs and a menu bar.
#FILE DUPLICATE FINDER MAPREDUCE CHECKSUM WINDOWS#
Dupe Clear is an open source duplicate file finder for Windows that can help you recover storage space. But that's not exactly easy to do, who has the time to pour over dozens of folders worth of data? This is why people rely on third-party programs. The solution is pretty obvious, keep one and delete the other.
#FILE DUPLICATE FINDER MAPREDUCE CHECKSUM PORTABLE#
This happens a lot to, especially when it comes to portable programs. Later you redownload it, and you got two copies now. Maybe you downloaded some application, and moved the installer to a different location. Here’s a well-written discussion about some of the transition problems from SmallData to BigData.Another reason why your hard drive could be nearing maximum capacity is due to duplicate files. RAM-based data access speed is always faster than disk-based systems, sometimes as much as 10 6 times faster, depending on technology and type of access. Keep it in memory: Once your data is in RAM, try to keep it there for as long as possible. Note that techniques that jump nodes are typically not SGE-friendly since the other nodes often can’t be scheduled correctly. If your workflow is amenable to NEVER hitting disk, it will be faster to pipeline the data from one analysis to the next using one of these techniques. Non-storage: ( pipes, named pipes or FIFOs, sockets, network operations, etc). The pack functions can optimally pack the variables using the shortest representation. In Perl and Python, you can dump the data in the native format and slurp it up again in the next utility. If your data is going to be shared with other programs written in the same language and they use the same internal data structure, why bother to export the data to different format. Non-relational DBs (NoSQLs): CouchDB server, MongoDB server, etcīinary dumps: (Perl’s Data::Dumper and pack, Python’s pickle, marshal, shelve, and struct.pack.
Relational DBs: ( SQLite - a relational engine only, PostgreSQL server, MySQL server and variants, etc) The utilities nco, ncview, Pytables, Vitables,


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
